Selective Laser Sintering: Paving the Way for Greener Manufacturing
In recent years, sustainability has become a global priority. As industries strive to reduce their environmental footprint, additive technologies such as Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) could play a crucial role in the quest for greener manufacturing. In this article, we will explore how SLS can contribute to sustainability and the benefits it offers towards a more eco-friendly approach to production.
Material Efficiency
One of the key sustainability advantages of Selective Laser Sintering is its efficient use of materials. Unlike subtractive manufacturing, SLS builds parts layer by layer with a laser using only the amount of material required. This additive approach minimizes waste, as the excess powder can be collected, sieved and reused (up to 90% depending on material) in the printing process. Subsequently, this allows manufacturers to reduce material consumption, resulting in cost savings and a more sustainable production cycle. Since the SLS process is more efficient the more densely the parts are stacked, software with nesting features can further optimize its material usage.
Elimination of Tooling
Traditional manufacturing methods often rely on complex tooling, such as molds and dies, which require significant resources and energy to produce. With SLS, the need for tooling is eliminated as the parts are made directly from digital designs. This reduces the associated costs and waste generated by tool production, storage and maintenance. Furthermore, the ability to create complex geometries without the need for tooling not only saves resources but also opens up new design possibilities, driving innovation and creativity in product development.
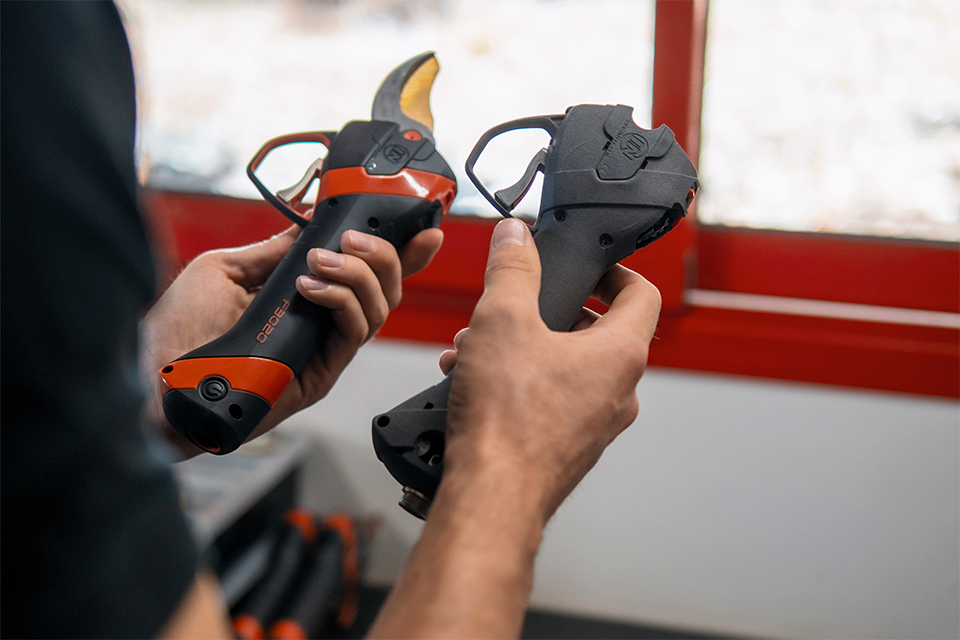

Customization and Just-in-Time
3D printing and SLS in particular are well suited for on-demand manufacturing, enabling the production of customized products tailored to meet specific customer needs. By eliminating the need for mass production and inventory storage, manufacturers can prevent overproduction and decrease scrap. This lean manufacturing approach reduces the environmental impact associated with surplus inventory and transportation, leading to a more sustainable supply chain. In addition, the ability to produce parts locally decreases the carbon footprint associated with long-distance shipping.
Multi-Use Plastics
Selective Laser Sintering could play a crucial role in shifting the paradigm from single-use plastics to multi-use alternatives. Traditional manufacturing often relies on injection molding to produce single-use plastic products, which contribute significantly to the global plastic waste. In contrast, SLS allows for the production of much more durable and high-quality polymer parts, intended for repeated use. Moreover, as older spare parts may no longer be available, 3D printing can effectively fill that gap to produce temporary or long term replacement pieces with a wide range of industrial-grade materials.
Conclusion
3D printing and Selective Laser Sintering in particular has a significant potential for greener manufacturing practices. By reducing material waste, eliminating tooling, enabling just-in-time production, and promoting recycling, SLS offers substantial environmental benefits. As industries continue to prioritize sustainability, this 3D printing process stands out as a powerful tool for moving towards a more eco-friendly future. By embracing the SLS technology, companies can not only improve their operational efficiency but also contribute to a more sustainable manufacturing ecosystem.
Need consulting?
Our team is happy to advise you and to begin your journey into the world of SLS. Contact us right away!