SLS vs. FDM: comparison of two 3D printing technologies
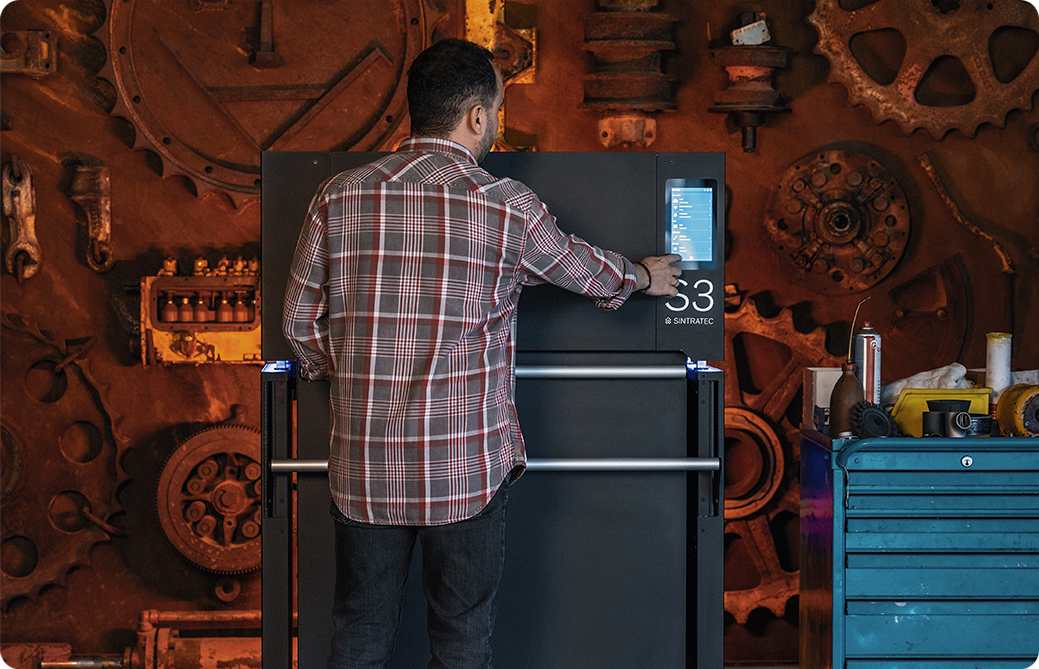
3D printing has made remarkable progress in recent years, revolutionizing the way we create prototypes, products, and complex designs that would not be possible with traditional manufacturing methods. In this article, we compare the two additive manufacturing technologies Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and look into their processes, applications, advantages, and limitations.
The SLS Process
In selective laser sintering (SLS), powdered thermoplastic materials are fused together using a laser. In this process, thin layers of powder are applied to a build platform, followed by the precise application of the laser, which selectively sinters and solidifies the particles into the desired shape. If you would like to learn more about SLS, have a look at this article.
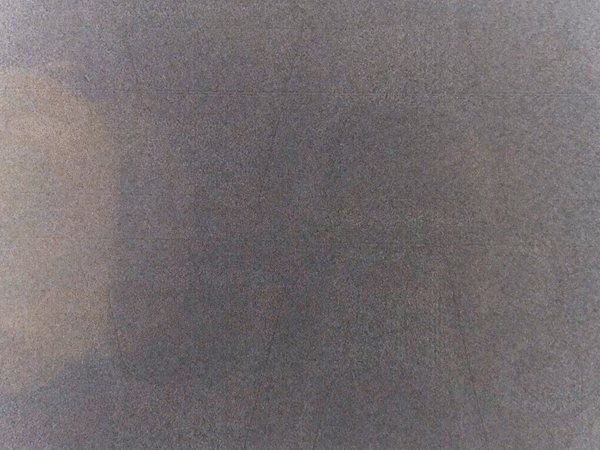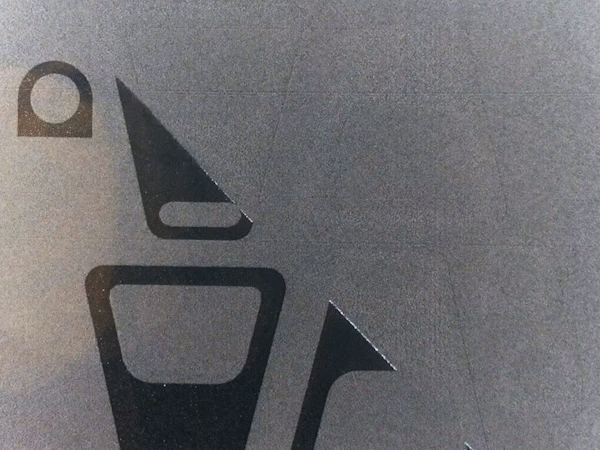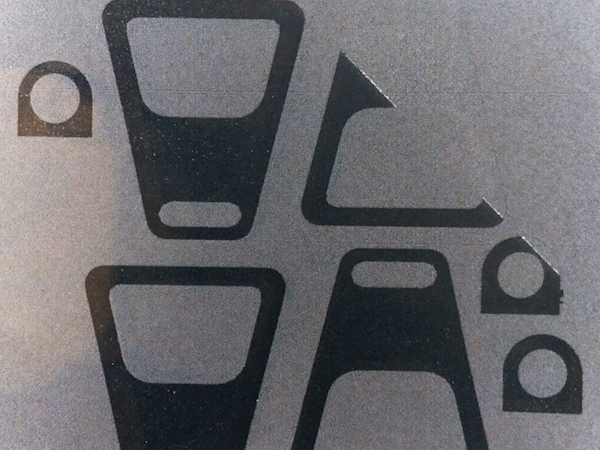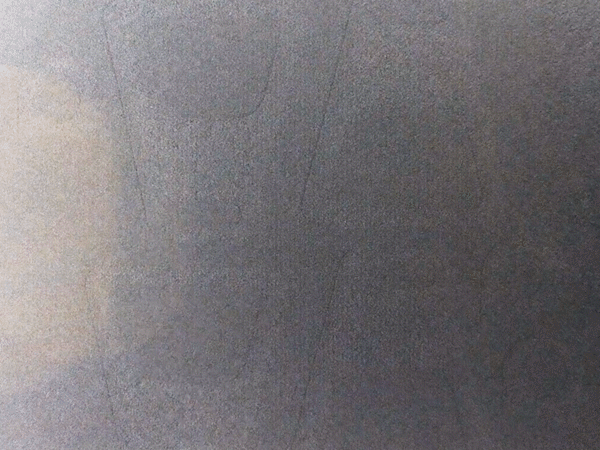
The FDM Process
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), also known as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), is another 3D printing process that has become increasingly popular, especially for private use. In FDM, thermoplastic filaments such as PLA, ABS, TPU, or other composites are heated to the melting point and extruded through a nozzle onto a build platform layer by layer.
Material Diversity
FDM offers a wide range of filaments, with a variety of colors standing out compared to SLS materials. Hobbyists are especially excited about the multitude of filaments available to create colorful 3D prints. Most materials are also attractively priced for home and small business use. The filaments are easy to handle and store, and the applications are numerous. However, the mechanical properties of FDM prints are rather limited compared to powder-based methods. In comparison, FDM 3D printers require a lower temperature to bring the material to the melting point, which negatively affects the temperature resistance of the printed component.
Mechanical properties
Compared to FDM, the SLS process scores particularly well at the material level. The higher melting temperature of polymers (185°C for PA12) makes the printed parts more heat resistant. This in turn opens the door to a wide range of applications involving thermal stress. Moreover, SLS powders offer greater options regarding mechanical properties, such as high tensile and compressive strength, which are more difficult to achieve in the FDM process. These superior mechanical properties are a clear plus for SLS, where even metal powders can be processed through novel methods like Cold Metal Fusion.
Level of Detail
One of the main advantages of SLS is the high level of detail achieved through the precision of the laser and the low layer thickness of the material deposited. As a result, parts have a better surface finish, are much more intricate, and can be reproduced more accurately due to low tolerances. In contrast, the nozzle through which the filament is extruded is limited to the smallest possible diameter and does not offer the precision of the laser, resulting in a coarser and rougher surface quality.
Support Structures
Unlike FDM printing, the SLS process requires no support structures as the unsintered material itself acts as a supporting structure. Furthermore, the unused powder is also recyclable up to 90% (depending on the material) and can be reprocessed into new printing powder by adding fresh powder. The support structures needed for FDM printing to create overhangs and more intricate geometries, on the other hand, cannot be reused after printing and ends up as waste. The points at which the support structures have to be removed further reduce the surface quality of the parts.
Applications for SLS
Both SLS and FDM offer unique capabilities for a wide range of applications. The superior material properties enables SLS to produce complex and functional components used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, engineering, and healthcare. Additionally, the ability to manufacture multiple work pieces in a single run makes SLS ideal for rapid prototyping of complex designs, as well as small to mid-sized production runs of consumer goods and customized items such as orthopedic insoles. With Fused Deposition Modeling, only a limited amount of parts can be produced simultaneously, making serial production significantly slower and usually uneconomical.

Applications for FDM
Due to its ease of use and lower price, FDM is much more accessible to hobbyists and small companies who want to implement their concepts quickly and cost-effectively. The technology is well suited for first iterations in rapid prototyping and is used in product design, architecture, art and design. In addition to the industries mentioned, FDM offers an excellent platform for educational purposes and as an entry into the world of 3D printing. Additionally, FDM can act as a bridging technology to test concepts before printing them through cost-intensive processes like SLS.

Summary
Both SLS and FDM are powerful 3D printing technologies with their own strengths and weaknesses. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of the project.
If the focus is on material properties, SLS is the right technology to produce prototypes, end products, and even small to mid-sized series with high quality and functionality. For hobbyists, SLS systems are usually not an option when investing in a 3D printer due to the high initial cost and material prices. However, the technology offers advantages for smaller companies, which we have explained in another article.
If material properties are not the main concern, FDM with its wide range of colorful filaments and low investment price offers an excellent platform for individuals, small businesses in various industries, and educational institutions.
In summary, all 3D printing technologies, especially SLS and FDM, will continue to drive innovation and expand their application areas. Future developments are expected to increase the already impressive performance of these methods and open up new horizons in the manufacturing industry.
Need consulting?
Our team is happy to advise you and to begin your journey into the world of SLS. Contact us right away!